How to Plant Pea Seeds A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the Right Pea Seeds
How to plant pea seeds – Selecting the right pea seeds is crucial for a successful harvest. Consider factors like your climate, soil type, and desired pea type (shelling or snap) to maximize your yield. The following table provides a comparison of various pea varieties, highlighting key characteristics to guide your selection.
Pea Variety Comparison
| Variety | Planting Time | Maturity (Days) | Growth Habit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar Snap Peas | Early Spring | 55-65 | Vining |
| Oregon Sugar Pod II | Spring | 60-70 | Bush |
| Lincoln | Spring | 65-75 | Vining |
| Early Alaska | Early Spring | 50-60 | Bush |
Pea Types and Characteristics
Shelling peas are grown for their dried seeds, which are harvested from the pods after the pods have matured and dried. Snap peas, on the other hand, are harvested while the pods are still young and tender, before the peas inside have fully developed. The choice depends on your preference.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Seeds
Climate plays a significant role. Choose early-season varieties for cooler climates and later-season varieties for warmer ones. Soil type influences drainage and nutrient availability. Well-draining soil is essential for peas. Finally, consider the desired yield; some varieties produce more peas per plant than others.
Preparing the Soil for Planting
Preparing the soil properly ensures optimal pea growth. Peas thrive in well-drained, slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-7.0) rich in organic matter. Amending the soil with compost or fertilizer improves its structure and nutrient content.
Ideal Soil Conditions and Preparation

Source: allotment-garden.org
Peas prefer loose, well-drained soil. Heavy clay soils should be amended with organic matter like compost to improve drainage and aeration. A soil test can determine the pH and nutrient levels, guiding fertilizer application. Adding well-rotted compost before planting enhances soil fertility and provides beneficial microbes.
Step-by-Step Raised Bed Preparation, How to plant pea seeds
- Choose a sunny location with at least six hours of sunlight per day.
- Clear the area of weeds, rocks, and debris.
- Construct a raised bed (optional, but recommended for better drainage and soil control).
- Fill the bed with a mixture of garden soil, compost, and a balanced fertilizer.
- Water the soil thoroughly to settle it before planting.
Sowing Pea Seeds
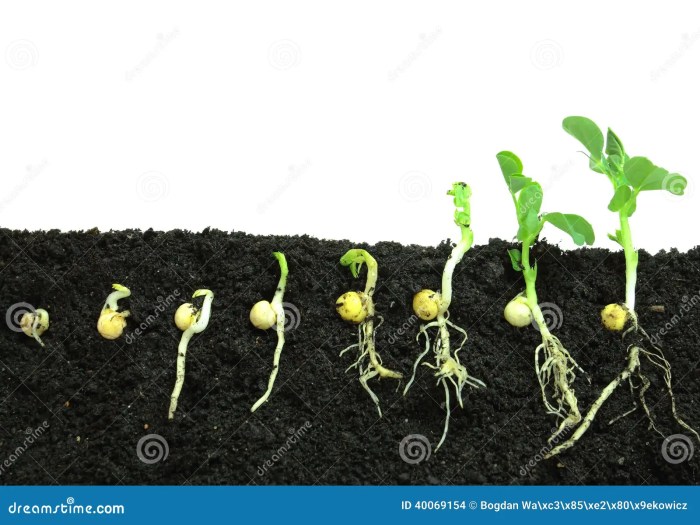
Direct sowing pea seeds into the ground is the most common method. Several techniques exist, each with its advantages. Correct depth and spacing are vital for successful germination and growth.
Direct Sowing Methods

Source: dreamstime.com
Broadcasting involves scattering seeds over the surface and lightly raking them in. Drilling involves sowing seeds in rows using a seed drill or by hand. Seed tapes, which contain seeds embedded in biodegradable paper, provide precise spacing and ease of planting.
Planting Depth and Spacing Illustration
Imagine a row of seeds planted approximately 1 inch deep and 2-3 inches apart. This spacing allows for adequate growth without overcrowding. For vining varieties, wider spacing might be beneficial. Bush varieties can be planted more closely together.
Watering and Maintaining Pea Plants
Consistent moisture is key to healthy pea growth. However, overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering stunts growth. A balanced watering schedule is crucial, adjusting based on weather conditions.
Watering Schedule and Moisture Management
Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods. Mulching helps retain soil moisture, reducing the frequency of watering. Avoid overhead watering, which can spread diseases. During hot spells, water early in the morning or late in the evening to minimize evaporation.
Protecting Pea Plants from Pests and Diseases
Pea plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Preventative measures and organic pest control methods can minimize damage and ensure a healthy crop.
Common Pests and Diseases and Preventative Measures
Common pests include aphids, pea weevils, and slugs. Diseases like powdery mildew and fusarium wilt can also affect pea plants. Crop rotation, choosing disease-resistant varieties, and maintaining good garden hygiene are essential preventative measures.
Organic Pest Control Methods
- Handpicking pests
- Using insecticidal soap
- Introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs
- Applying neem oil
Harvesting Pea Crops
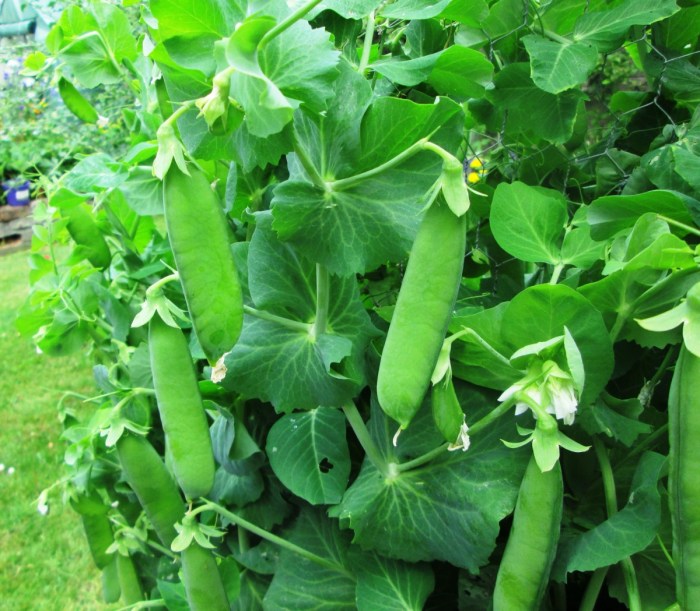
Knowing when and how to harvest peas maximizes their flavor and quality. The harvesting technique differs depending on whether you’re growing shelling peas or snap peas.
Signs of Maturity and Harvesting Techniques

Source: saymedia-content.com
Snap peas are ready for harvest when the pods are plump and bright green. Shelling peas are ready when the pods are dry and the peas inside are fully developed. Harvest regularly to encourage continued production. Gently pull or snap the pods from the plant, avoiding damage to the vines.
Post-Harvest Handling and Storage
Snap peas should be refrigerated and consumed within a few days. Shelling peas can be dried for longer storage or frozen for later use. Proper handling and storage ensure the peas maintain their quality and freshness.
Q&A: How To Plant Pea Seeds
Can I plant pea seeds indoors?
Yes, you can start pea seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last expected frost. Use small pots and transplant outdoors once the danger of frost has passed.
How long do peas take to grow?
The time from planting to harvest varies depending on the variety, but generally ranges from 50 to 75 days.
Planting pea seeds involves choosing a sunny spot and preparing loose soil. Ensure proper spacing for optimal growth, then gently sow the seeds at the recommended depth. For a similar root vegetable, you might find the detailed guide on how to plant carrots from seed helpful, as understanding root vegetable planting techniques can be beneficial for peas as well.
Remember to water regularly and provide adequate support for climbing pea varieties.
What should I do if my pea plants are wilting?
Wilting can indicate underwatering or overwatering. Check the soil moisture; water deeply if dry, but ensure good drainage to prevent root rot.
What are the signs of pea plant maturity?
The pods will become plump and full, and the peas inside will be well-developed and easily visible through the pod’s skin.