How to Plant a Strawberry Seed
Growing Strawberries from Seed: A Comprehensive Guide: How To Plant A Strawberry Seed
How to plant a strawberry seed – Cultivating strawberries from seed offers a rewarding experience, allowing you to nurture these delightful fruits from their very beginnings. While it requires more patience than starting with established plants, the process is achievable with careful attention to detail. This guide will walk you through each step, from selecting the right seeds to transplanting your thriving seedlings.
Seed Selection and Preparation, How to plant a strawberry seed

Source: thespruce.com
Choosing high-quality seeds and preparing them correctly significantly impacts germination success. Several factors influence seed viability, including seed age and storage conditions. Proper scarification, where necessary, can improve germination rates by weakening the seed coat.
| Strawberry Type | Germination Rate | Seed Starting Suitability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| June-bearing | Moderate | Good | Produces a large crop once a year. |
| Everbearing | Moderate to High | Good | Produces smaller crops throughout the growing season. |
| Alpine | High | Excellent | Produces smaller berries continuously; well-suited for containers. |
| Day-neutral | Moderate | Good | Produces fruit throughout the growing season, regardless of day length. |
A well-draining seed starting mix is crucial. A suitable blend consists of equal parts peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite. This combination provides excellent aeration and moisture retention.
Sowing the Seeds
Sowing strawberry seeds requires precision and gentleness. The optimal depth and spacing are critical for successful germination and seedling development. Overcrowding can lead to competition for resources and stunted growth.
- Fill seed trays or small pots with the prepared seed starting mix, leaving about ½ inch from the top.
- Scatter seeds evenly across the surface, ensuring proper spacing (approximately ½ inch apart).
- Gently cover the seeds with a thin layer (1/8 inch) of the seed starting mix.
- Water gently using a fine mist to avoid disturbing the seeds.
Germination Environment
Creating the right environment for germination is paramount. Strawberry seeds need consistent warmth, moisture, and light to sprout successfully. A humid environment significantly enhances germination rates.
- Maintain a temperature between 65-75°F (18-24°C).
- Keep the seed starting mix consistently moist but not soggy.
- Cover the seed tray with a plastic dome or use a humidity tray to maintain high humidity.
- Provide 12-16 hours of light per day using grow lights, placed a few inches above the seedlings.
Seedling Care
Careful watering and monitoring are essential for healthy seedling development. Recognizing signs of healthy and unhealthy seedlings allows for timely intervention.
- Water seedlings regularly, ensuring the soil remains moist but not waterlogged.
- Healthy seedlings exhibit vibrant green leaves and strong stems.
- Unhealthy seedlings may appear wilted, yellowed, or show signs of disease.
Potential problems and solutions:
- Damping-off: Overwatering; improve drainage and ventilation.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Yellowing leaves; use a balanced fertilizer.
- Pest infestations: Inspect regularly; use appropriate pesticides if needed.
Transplanting Seedlings

Source: tasteofhome.com
Transplanting involves carefully moving seedlings to larger containers or directly into the garden. The timing depends on seedling size and weather conditions.
A healthy, ready-to-transplant strawberry seedling will have several true leaves, a strong stem, and a well-developed root system. The leaves will be a deep green color, indicating vigorous growth and health.
Ongoing Care After Transplanting
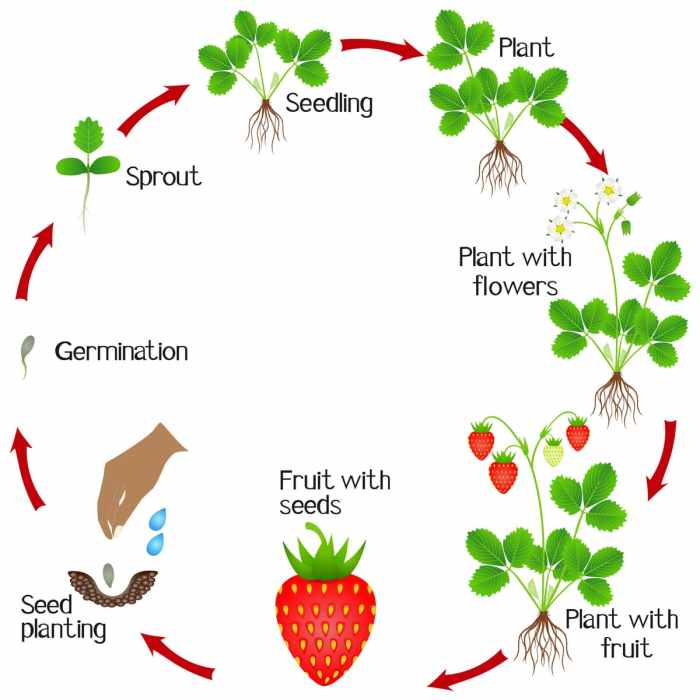
Source: strawberryplants.org
Planting strawberry seeds involves starting them indoors in small pots with well-draining soil. The process is quite similar to growing other vegetables; for example, understanding the basics of planting strawberries can help you transition to learning how to plant other crops, such as how to plant green pepper seeds , which also requires careful attention to soil moisture and sunlight.
Once you’ve mastered these fundamental techniques, you’ll be well-equipped to cultivate a thriving strawberry patch.
Continued care after transplanting ensures the survival and healthy growth of your strawberry plants. Regular watering, fertilization, and pest control are crucial.
- Water regularly, especially during dry periods.
- Fertilize with a balanced fertilizer according to package instructions.
- Remove weeds to prevent competition for resources.
- Monitor for pests and diseases; take appropriate measures if needed.
- Protect plants from extreme weather conditions using row covers or other protective measures.
Helpful Answers
Can I use store-bought strawberries to get seeds?
While possible, seeds from store-bought strawberries may have lower germination rates due to hybrid varieties and possible treatment. It’s best to use seeds specifically labeled for planting.
How long does it take for strawberry seeds to germinate?
Germination time varies depending on the variety and conditions, but generally takes 2-4 weeks. Some may take longer.
What should I do if my seedlings are leggy?
Leggy seedlings indicate insufficient light. Increase light exposure using grow lights or move seedlings closer to a natural light source.
What are the signs of healthy strawberry seedlings?
Healthy seedlings exhibit vibrant green leaves, strong stems, and a well-developed root system. They should be growing steadily and showing no signs of disease or pest infestation.