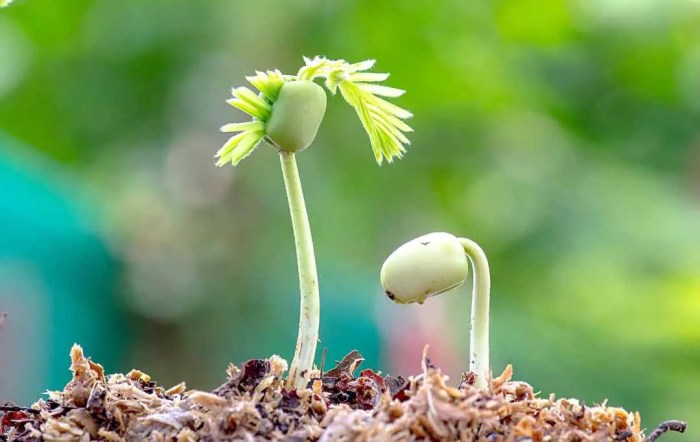
How to Plant a Tamarind Seed
Sourcing Tamarind Seeds

Source: bedgardening.com
How to plant a tamarind seed – Securing viable tamarind seeds is the crucial first step in successful cultivation. The source and quality of your seeds significantly impact germination rates and the overall health of your seedlings. This section will explore different methods of obtaining tamarind seeds, comparing their advantages and disadvantages.
Obtaining Viable Tamarind Seeds
There are two primary ways to obtain tamarind seeds: purchasing them from reputable suppliers or harvesting them directly from ripe tamarind fruit. Purchased seeds often offer convenience and a higher likelihood of viability, particularly if sourced from specialized nurseries. However, harvesting your own seeds allows for greater control over the seed’s origin and genetic characteristics.
Extracting Seeds from Tamarind Fruit
Extracting tamarind seeds requires careful handling to avoid damaging them. Begin by selecting ripe, plump tamarind pods. Open the pod carefully, revealing the sticky pulp surrounding the seeds. Gently remove the pulp using water, ensuring not to crush the seeds. Allow the seeds to dry completely in a well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight, before proceeding with the planting process.
A soft brush can aid in removing the remaining pulp.
Seed Source Comparison
The choice between purchased and harvested seeds depends on your priorities. Purchased seeds offer guaranteed viability and potentially faster germination, but may be more expensive and limit your selection of specific tamarind varieties. Harvested seeds offer cost-effectiveness and the opportunity to select seeds from desired trees, but may have lower germination rates due to potential damage during harvesting or improper storage.
Seed Preparation and Pre-Sowing Treatment

Source: sardabiopolymers.com
Proper seed preparation is essential for maximizing germination success. Tamarind seeds possess a hard seed coat that can hinder germination. Therefore, pre-sowing treatments, such as scarification or soaking, are necessary to break seed dormancy and improve germination rates.
Cleaning and Preparing Tamarind Seeds
After extraction, thoroughly clean the seeds to remove any remaining pulp or debris. This prevents fungal growth and ensures a clean planting environment. A gentle scrubbing with water and a soft brush is recommended. Allow the cleaned seeds to dry completely before proceeding with scarification or soaking.
Methods for Breaking Seed Dormancy
Scarification, a process of weakening the seed coat, is often employed to enhance germination. This can be achieved through mechanical methods, such as gently nicking the seed coat with a file or sandpaper, or through chemical methods using concentrated sulfuric acid (this requires caution and protective gear). Soaking the seeds in warm water for 12-24 hours can also help soften the seed coat and promote germination.
Soaking Tamarind Seeds
Soaking tamarind seeds in warm water for 12-24 hours is a common practice to improve germination rates. This helps soften the hard seed coat, allowing for easier water absorption and faster germination. Ensure the water is not too hot, as this can damage the seeds. After soaking, drain the water and allow the seeds to air dry slightly before planting.
Choosing the Right Planting Medium and Container
The choice of planting medium and container significantly impacts tamarind seed germination and seedling growth. A well-draining, nutrient-rich soil mix provides the optimal environment for successful germination. Selecting the appropriate container ensures adequate space for root development and easy transplanting.
Ideal Soil Composition for Germination
Tamarind seedlings thrive in well-drained, slightly acidic soil. A mix of potting soil, compost, and perlite is ideal. The perlite improves drainage and aeration, preventing waterlogging, while the compost adds essential nutrients.
| Mix Name | Composition | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Mix | 2 parts potting soil, 1 part compost, 1 part perlite | Good drainage, nutrient-rich | May require additional fertilization |
| Enriched Mix | 2 parts potting soil, 1 part compost, 1 part perlite, 0.5 part vermiculite | Excellent drainage and aeration, added nutrients | More expensive |
| Sandy Mix | 3 parts potting soil, 2 parts coarse sand, 1 part perlite | Excellent drainage | May require more frequent watering and fertilization |
| Coco Coir Mix | 2 parts coco coir, 1 part perlite, 1 part compost | Water retention, good aeration | May require additional nutrients |
Selecting Appropriate Containers
Small pots or seed trays are suitable for germinating tamarind seeds. Ensure the containers have drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Individual pots are preferable as they minimize root disturbance during transplanting.
Designing a Planting Container
A suitable container should be at least 4 inches in diameter and depth to accommodate the initial growth of the tamarind seedling. The container material should be breathable (e.g., terracotta) to allow for proper aeration. Drainage holes are essential to prevent root rot.
Planting Tamarind Seeds: Step-by-Step Guide
Planting tamarind seeds involves a straightforward process, but attention to detail is crucial for maximizing germination success. The following steps provide a clear guide to ensure your seeds have the best chance of sprouting.
- Prepare the Container and Soil: Fill the chosen container with the prepared soil mix, leaving about half an inch of space from the top. Gently moisten the soil, ensuring it’s not waterlogged.
- Create Planting Holes: Using your finger or a small dibber, create small holes approximately 1cm deep. The hole should be slightly larger than the tamarind seed. The soil should be moist but not muddy; a crumbly texture is ideal.
- Place the Seeds: Carefully place one tamarind seed in each hole, ensuring the pointed end faces downwards. Avoid overcrowding the seeds.
- Cover the Seeds: Gently cover the seeds with soil, ensuring they are completely buried. Avoid pressing down too firmly, as this can damage the delicate seeds.
- Water Gently: Water the soil gently using a watering can with a fine rose, ensuring the soil is evenly moistened. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to fungal diseases.
- Label and Place: Label the container with the planting date and seed variety. Place the container in a suitable location that provides optimal growing conditions.
Providing Optimal Growing Conditions
Tamarind seed germination and seedling growth are heavily influenced by environmental factors. Maintaining optimal conditions is crucial for successful cultivation. This section will discuss the ideal light, temperature, and humidity levels, as well as proper watering techniques.
Ideal Environmental Conditions
Tamarind seeds germinate best in warm temperatures (25-30°C or 77-86°F). They require ample sunlight (at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily). High humidity levels (around 60-70%) are beneficial for germination and early seedling growth. A warm, humid greenhouse or a sunny location protected from strong winds is ideal.
Proper Watering Techniques
Consistent moisture is crucial, but overwatering should be avoided. Water the soil thoroughly when the top inch feels dry to the touch. Allow the soil to drain completely after watering, preventing waterlogging which can lead to root rot. Use a watering can with a fine rose to avoid disturbing the soil and seeds.
Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges include slow germination, fungal diseases (damping-off), and pest infestations. Slow germination can be addressed by ensuring proper seed preparation and optimal environmental conditions. Fungal diseases can be prevented through proper soil drainage and avoiding overwatering. Pest infestations can be managed through the use of organic pest control methods.
Seedling Care and Transplanting
Once tamarind seeds germinate, consistent care is crucial for healthy seedling growth. This includes proper watering, fertilization, and pest control. Eventually, the seedlings will need to be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the ground.
Seedling Care
Regular watering is essential, keeping the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Fertilize the seedlings with a balanced liquid fertilizer every 2-3 weeks, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Monitor for pests and diseases, implementing appropriate control measures as needed. Regularly inspect the seedlings for any signs of stress or disease.
Transplanting Tamarind Seedlings
Once the seedlings develop several true leaves (typically 4-6 weeks after germination), they can be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the ground. Handle the seedlings carefully to avoid damaging their roots. When transplanting into the ground, ensure the soil is well-drained and the location receives ample sunlight.
Tamarind Seedling Growth Timeline, How to plant a tamarind seed
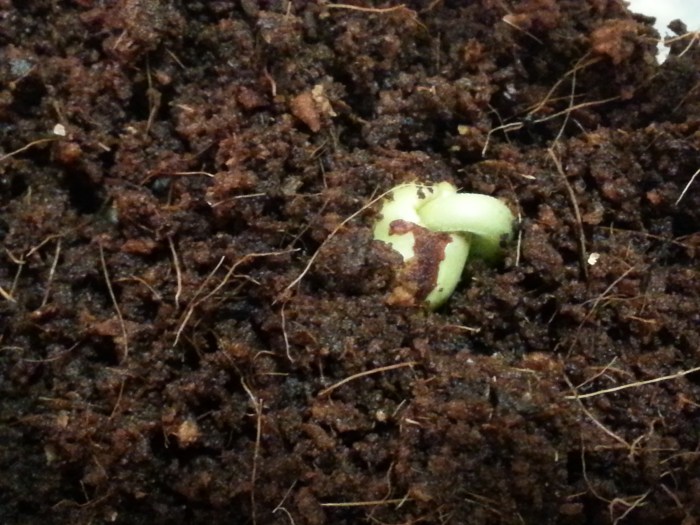

Source: gardenisto.com
- Weeks 1-4: Germination and emergence of cotyledons. Maintain consistent moisture and warmth.
- Weeks 4-8: Development of true leaves. Begin fertilizing and monitor for pests.
- Weeks 8-12: Seedlings become more robust. Consider transplanting into larger containers.
- Months 3-6: Seedlings develop a stronger root system. Transplant into the ground if conditions are suitable.
- Months 6-12: Continued growth and establishment. Regular watering and fertilization are important.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Despite careful planning, certain issues may arise during tamarind seed germination and seedling growth. Understanding these challenges and their solutions is crucial for successful cultivation. This section covers common problems and their preventative measures.
Common Issues and Solutions
Damping-off: This fungal disease causes seedlings to rot at the base. Ensure good soil drainage and avoid overwatering. Use a fungicide if necessary.
Pest Infestations: Aphids, mealybugs, and other pests can damage seedlings. Use organic pest control methods, such as insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Yellowing leaves or stunted growth may indicate nutrient deficiencies. Use a balanced fertilizer to provide essential nutrients.
Slow Germination: Ensure proper seed preparation and optimal growing conditions. Check for seed viability.
Successfully germinating a tamarind seed requires a bit of patience; soaking it before planting is key. Interestingly, the process shares some similarities with growing other plants from seed, such as the meticulous approach needed when learning how to plant peonies from seed. Understanding seed stratification techniques, beneficial for both peonies and tamarinds, improves germination rates.
Ultimately, consistent moisture and the right temperature are crucial for a healthy tamarind seedling.
Preventative Measures
Using high-quality seeds, providing optimal growing conditions, maintaining good soil drainage, and implementing preventative pest and disease control measures significantly reduce the risk of problems.
Quick FAQs: How To Plant A Tamarind Seed
Can I use tamarind seeds from store-bought tamarind paste?
While possible, the viability of seeds from paste is questionable due to processing. Freshly harvested seeds are recommended.
How long does it take for a tamarind seed to germinate?
Germination time varies, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months, depending on conditions and seed viability.
What should I do if my tamarind seedling develops fungal diseases?
Treat with a suitable fungicide following label instructions. Ensure good air circulation and avoid overwatering to prevent fungal growth.
How often should I water my tamarind seedling?
Water regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adjust watering frequency based on climate and soil conditions.