How to Plant Green Bell Pepper Seeds
Starting Green Bell Pepper Seeds Indoors
How to plant green bell pepper seeds – Successfully growing green bell peppers begins with starting seeds indoors. This process allows for earlier harvests and better control over the growing environment. Proper seed starting techniques are crucial for healthy seedlings and a bountiful yield.
Ideal Timing for Indoor Seed Starting
The ideal time to start green bell pepper seeds indoors depends heavily on your climate. Generally, you should begin 6-8 weeks before the last expected frost in your area. This allows the seedlings ample time to mature before transplanting outdoors. For example, if your last frost is typically around May 15th, you should start your seeds around the end of March or early April.
Preparing the Seed Starting Mix
A well-draining seed starting mix is essential for healthy germination. A good mix typically consists of a blend of peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite. These components provide excellent drainage, aeration, and moisture retention. Sterilizing the mix helps prevent damping-off disease, a common problem in seed starting. This can be achieved by microwaving the mix for several minutes or baking it in the oven at a low temperature for about 30 minutes.
Sowing Green Bell Pepper Seeds
Sow seeds about ¼ inch deep and 1 inch apart in your chosen seed starting container. Gently cover the seeds with the seed starting mix. Keep the mix consistently moist but not soggy. Ensure good air circulation to prevent fungal growth.
Optimal Indoor Germination Environment
Green bell pepper seeds germinate best in warm temperatures, ideally between 70-80°F (21-27°C). Maintaining consistent humidity is also important. You can achieve this by covering the seed tray with a clear plastic dome or humidity dome, or by placing the tray in a plastic bag. Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent mold growth. Once seedlings emerge, remove the covering gradually.
Seed Starting Container Comparison, How to plant green bell pepper seeds
| Container Type | Pros | Cons | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed Trays | Cost-effective, allows for efficient space utilization | Requires transplanting, potential for root disturbance | Best for large-scale seed starting |
| Peat Pots | Easy transplanting, minimizes root disturbance | Can be more expensive, may dry out faster | Ideal for individual seedlings |
| Cell Packs | Good balance between cost and convenience, minimizes root disturbance | Slightly more expensive than seed trays | Versatile option for various seed starting needs |
| Individual Seed Starting Cups | Easy handling, minimal root disturbance, easy transplanting | Can be expensive, takes up more space | Suitable for delicate seedlings and larger seeds |
Seedling Care: How To Plant Green Bell Pepper Seeds
Providing proper care to your green bell pepper seedlings is crucial for healthy growth and development. This involves careful attention to watering, lighting, and disease prevention.
Watering Green Pepper Seedlings
Water seedlings regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Underwatering will cause wilting and stunted growth, while overwatering can lead to root rot. Allow the top inch of soil to dry slightly between waterings. Check the soil moisture regularly by touching it – if it feels dry, it’s time to water.
Importance of Light for Seedling Growth
Green bell pepper seedlings require ample light for healthy growth. Ideally, they need at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day. If natural sunlight is insufficient, supplement with grow lights, ensuring they are positioned appropriately to prevent burning or stretching.
Common Seedling Diseases and Pests
Common seedling diseases include damping-off and various fungal infections. Pests like aphids and spider mites can also infest seedlings. Preventative measures include sterilizing the seed starting mix, ensuring good air circulation, and regularly inspecting seedlings for signs of disease or pests. Treating infestations promptly with appropriate insecticides or fungicides is crucial.
Hardening Off Seedlings
Before transplanting outdoors, gradually acclimate seedlings to outdoor conditions through a process called hardening off. This involves gradually exposing them to more sunlight, wind, and temperature fluctuations over a period of 7-10 days.
Planting green bell pepper seeds involves starting them indoors in seed trays, ensuring proper soil moisture. Before you know it, you’ll be tending to your thriving pepper plants, but first, you might be wondering about your lawn; it’s a good time to check can i plant grass seed now to ensure optimal timing. Once your grass is sorted, you can return to nurturing those pepper seedlings, eventually transplanting them outdoors for a bountiful harvest.
Fertilizing Green Pepper Seedlings
Begin fertilizing seedlings once they have developed their first true leaves. Use a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength. Fertilize every 1-2 weeks, following the fertilizer’s instructions carefully. Avoid over-fertilizing, which can burn the seedlings.
Transplanting Green Bell Peppers Outdoors
Once the danger of frost has passed and seedlings are strong enough, it’s time to transplant them outdoors. Proper preparation and technique are crucial for successful transplanting.
Ideal Soil Conditions
Green bell peppers thrive in well-drained, slightly acidic soil with a pH of 6.0-6.8. Amend heavy clay soils with organic matter like compost to improve drainage and aeration. Sandy soils may benefit from the addition of peat moss to increase water retention.
Transplanting Process
Dig holes slightly larger than the root balls of the seedlings. Space plants 18-24 inches apart to allow for adequate growth. Gently remove seedlings from their containers, avoiding root damage. Plant seedlings at the same depth they were growing in their containers. Water thoroughly after transplanting.
Preparing the Planting Site
Clear the planting area of weeds and debris. Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve fertility and drainage. Consider using raised beds for better drainage in heavy clay soils.
Trellises or Cages for Support
Using trellises or cages can provide support for pepper plants, especially taller varieties, preventing them from sprawling and improving air circulation. This can help prevent fungal diseases and improve fruit production. However, they require additional setup and maintenance.
- Prepare the soil by tilling and amending it with compost.
- Dig holes appropriately spaced for the seedlings.
- Gently remove seedlings from their containers.
- Plant seedlings at the same depth as in containers.
- Water thoroughly after planting.
- Consider adding mulch around the plants to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Outdoor Care and Maintenance
Providing consistent care to your outdoor green bell pepper plants is crucial for maximizing yield and maintaining plant health.
Watering Techniques
Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods. Avoid overhead watering, which can encourage fungal diseases. Drip irrigation or soaker hoses are excellent options for efficient and targeted watering.
Weed Control
Regularly remove weeds around pepper plants to reduce competition for nutrients and water. Mulching helps suppress weed growth and retain soil moisture.
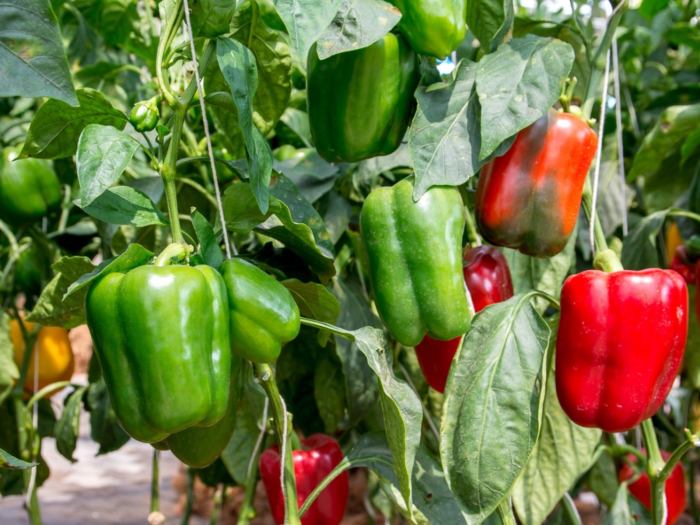
Regular Fertilization

Source: gardeningknowhow.com
Continue fertilizing green bell peppers throughout the growing season. Use a balanced fertilizer, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Side-dress the plants with fertilizer every 4-6 weeks, avoiding contact with the stems.
Common Diseases and Pests
Common diseases include blossom-end rot, bacterial spot, and various fungal diseases. Pests like aphids, whiteflies, and flea beetles can also infest pepper plants. Monitor plants regularly for signs of disease or pests, and address infestations promptly with appropriate control measures.
Green Bell Pepper Growth Stages
Here’s a text-based illustration of the typical growth stages:
- Seed Germination: The seed sprouts and a small root emerges.
- Seedling Stage: The plant develops its first true leaves.
- Vegetative Growth: The plant grows vigorously, producing more leaves and stems.
- Flowering Stage: Flowers appear, and pollination occurs.
- Fruit Development: Small peppers begin to develop and grow.
- Maturity: Peppers reach their full size and color, ready for harvest.
Harvesting Green Bell Peppers
Knowing when and how to harvest green bell peppers is essential for maximizing yield and quality.
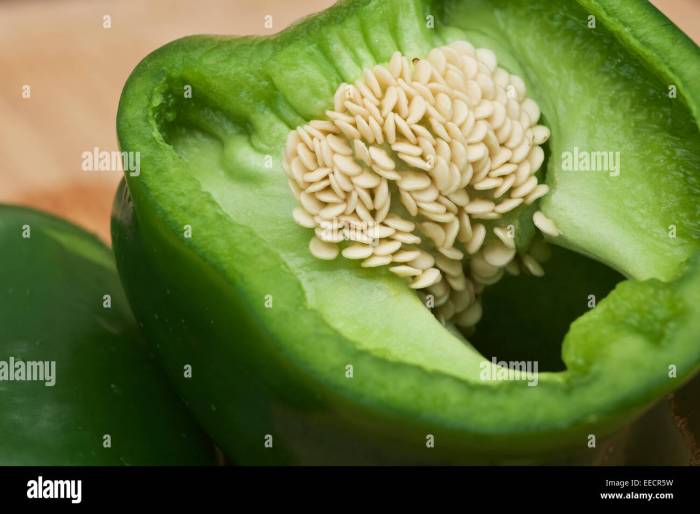
Signs of Ripe Green Bell Peppers

Source: alamy.com
Green bell peppers are ready for harvest when they have reached their desired size and have a firm, glossy skin. The peppers should be fully developed, with a rich green color.
Harvesting Technique
Use a sharp knife or pruning shears to harvest green bell peppers, cutting them from the plant at the stem. Avoid pulling or twisting the peppers, as this can damage the plant.
Storage Methods
Store harvested green bell peppers in the refrigerator at temperatures around 35-40°F (2-4°C). They will stay fresh for about a week to ten days.
Extending the Harvesting Season
Proper plant care, including consistent watering and fertilization, contributes to a longer harvesting season. Consider using row covers to protect plants from frost in cooler climates.
Harvesting Technique Comparison
| Harvesting Method | Yield | Plant Health | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting at the stem | High | Minimal impact | Most common, efficient, and minimizes plant damage |
| Pulling the pepper | High | Potential for damage | Faster, but risks damaging the plant |
| Using pruning shears | High | Minimal impact | Clean cut, reduces risk of disease, but slower |
FAQ Overview
Can I use tap water to water my pepper seedlings?
It’s best to use filtered or rainwater, as tap water may contain chlorine or other chemicals that can harm seedlings. Let tap water sit out overnight to allow chlorine to dissipate, but filtered water is always preferred.
How often should I fertilize my outdoor pepper plants?
Fertilize every 2-3 weeks with a balanced fertilizer, following package instructions. Avoid over-fertilizing, which can harm the plants.
What should I do if I see pests on my pepper plants?
Inspect plants regularly. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil for common pests like aphids. For severe infestations, consult a gardening expert.
When is the best time to harvest green bell peppers?
Harvest when peppers are firm and have reached their desired size, typically 3-4 inches long. The color will depend on the pepper variety; some are harvested green, others when they turn red or other colors.