How to Grow Apple Plants From Seeds
Growing Apple Trees from Seed: How To Grow Apple Plant From Seeds
Source: ftcdn.net
How to grow apple plant from seeds – Growing apple trees from seed is a rewarding but challenging endeavor. Unlike simply planting a cutting or buying a sapling, starting from seed offers a unique connection to the tree’s lifecycle and the potential for developing new varieties. However, it’s crucial to understand that apple trees grown from seed rarely produce fruit identical to the parent tree. The resulting tree will likely have different characteristics, potentially including a different taste and appearance of the fruit.
Seed Selection and Preparation, How to grow apple plant from seeds
Selecting healthy, ripe seeds is paramount for successful germination. Seeds from fully mature, organically grown apples are ideal. Avoid seeds from apples treated with growth regulators or pesticides. The preparation process involves cleaning and stratification, a crucial step mimicking the natural winter conditions seeds experience before germination.
- Seed Collection and Cleaning: Extract seeds from ripe apples, rinsing them thoroughly to remove any fruit pulp. Allow them to dry completely before proceeding.
- Stratification: This process involves exposing seeds to cold, moist conditions for several months. Mix the cleaned seeds with slightly moist vermiculite or peat moss in a sealed container. Refrigerate for 3-4 months at approximately 35-40°F (2-4°C). This mimics the natural winter dormancy period.
| Variety | Germination Rate | Planting Time | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gala | 60-70% | Late Winter/Early Spring | Medium |
| Fuji | 50-60% | Late Winter/Early Spring | Medium |
| Honeycrisp | 40-50% | Late Winter/Early Spring | Hard |
| Granny Smith | 65-75% | Late Winter/Early Spring | Medium |
Sowing and Germination
The success of germination depends on providing the ideal environment for the seeds. This includes selecting the appropriate soil, sowing method, and maintaining proper moisture levels.
- Soil Preparation: Use a well-draining seed-starting mix or a blend of potting soil, perlite, and vermiculite. Ensure the soil is loose and aerated to allow for root development.
- Sowing Methods: Seeds can be sown directly outdoors after the last frost or started indoors in seed trays or pots. Direct sowing requires careful consideration of timing and protection from extreme weather.
- Watering and Drainage: Maintain consistent moisture, but avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot. Ensure good drainage to prevent waterlogging.
Diagram illustrating optimal depth and spacing: Imagine a small seed sown about 1/4 inch deep, with about 1 inch of space between individual seeds in a row, and rows spaced approximately 2 inches apart. This allows for adequate spacing for root development.
Seedling Care and Growth
Providing the right care for apple seedlings is crucial for their healthy growth. This includes a regular watering and fertilizing schedule, protection from diseases and pests, and ensuring sufficient sunlight and air circulation.
- Watering and Fertilizing: Water regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Use a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength every 2-3 weeks during the growing season.
- Sunlight and Air Circulation: Apple seedlings require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Ensure good air circulation to prevent fungal diseases.
- Apple Scab (Venturia inaequalis): A fungal disease causing dark lesions on leaves and fruit. Treatment involves fungicides and good sanitation.
- Powdery Mildew (Podosphaera leucotricha): A fungal disease causing a white powdery coating on leaves and fruit. Treatment involves fungicides and improving air circulation.
- Aphids: Small insects that suck sap from leaves and stems. Treatment involves insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Transplanting and Aftercare

Source: shapeof.com
Once seedlings reach a certain size, they need to be transplanted to larger containers or directly into the ground. This requires careful handling to avoid damaging the delicate root system. Subsequent care involves protection from weather and regular pruning.
- Transplanting: Transplant seedlings into larger containers when they become root-bound or directly into the ground after the last frost, ensuring adequate spacing between trees.
- Protection from Harsh Weather: Young apple trees are vulnerable to frost, strong winds, and extreme temperatures. Provide protection using windbreaks, mulch, or protective coverings.
- Pruning and Shaping: Regular pruning is essential for shaping the tree, promoting healthy growth, and maximizing fruit production. Learn basic pruning techniques to remove dead or damaged branches and maintain a balanced structure.
- Grafting: Grafting allows you to combine the desirable traits of different apple varieties. This technique involves carefully joining a scion (cutting from a desired variety) to the rootstock (the seedling).
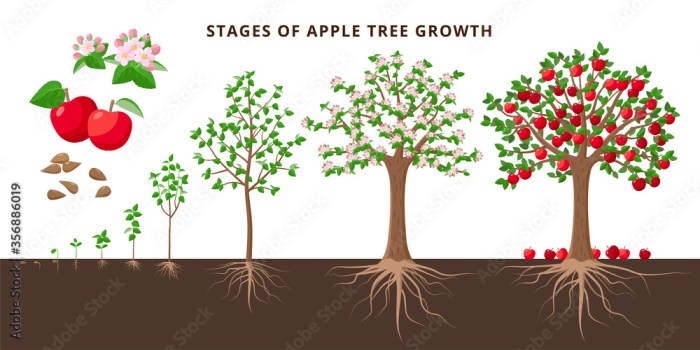
Understanding Apple Tree Growth
Apple trees go through distinct stages of growth, from a small seedling to a mature fruiting tree. Understanding these stages helps in providing appropriate care at each phase. Factors such as climate and soil significantly influence their growth.
The timeline for an apple tree to bear fruit from seed is highly variable, ranging from 5 to 15 years, depending on the variety, growing conditions, and other factors. Some varieties are known for faster fruiting while others may take much longer.
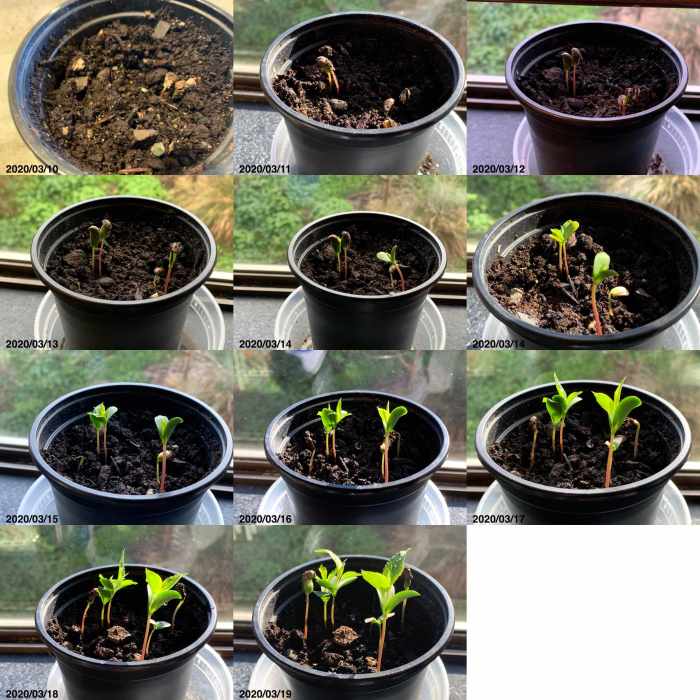
Visual Guide to Apple Seed Germination
An apple seed consists of three main parts: the seed coat (protective outer layer), the endosperm (nutrient-rich tissue providing energy for the embryo), and the embryo (the miniature plant). The embryo contains the radicle (the first root) and the plumule (the first shoot).
Visual representation of germination stages: Imagine a series of illustrations showing the seed imbibing water, the seed coat cracking, the radicle emerging, and finally, the plumule pushing upwards, developing leaves. These stages are depicted in a sequence, illustrating the process from dormancy to seedling emergence.
Ideal conditions for germination are illustrated as a graphic showing optimal temperature (around 65-75°F or 18-24°C), moisture (consistent moisture, but not waterlogged), and light (indirect light is ideal for seedlings).
Troubleshooting Common Problems

Source: vecteezy.com
Growing apple trees from seed can present several challenges. Identifying and addressing these problems promptly is crucial for successful cultivation.
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Seedlings | Poor soil, insufficient light, insufficient water | Improve soil quality, increase light exposure, adjust watering schedule | Use quality seed-starting mix, provide adequate light, and monitor moisture levels. |
| Fungal Diseases | Poor air circulation, excessive moisture | Apply fungicides, improve air circulation, reduce watering | Ensure good air circulation, avoid overwatering, and use disease-resistant varieties. |
| Pest Infestations | Presence of insects or other pests | Use insecticidal soap, neem oil, or other appropriate pest control methods | Regular monitoring, preventative measures, and using pest-resistant varieties. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of apple seeds germinate best?
Growing apple trees from seed requires patience; it’s a lengthy process unlike the quicker establishment of a lawn. Interestingly, the principles of minimal soil disturbance are similar; for instance, preparing the seedbed for your apple seeds mirrors the techniques described in this guide on how to plant grass seed without tilling , focusing on gentle soil preparation to avoid damaging delicate roots.
This careful approach ensures optimal germination and growth for both apples and grass.
Seeds from healthy, ripe apples generally have the highest germination rates. Avoid using seeds from store-bought apples that may have been treated to prevent germination.
How long does it take for an apple tree grown from seed to bear fruit?
It can take anywhere from 5 to 15 years, or even longer, for an apple tree grown from seed to produce fruit. This is significantly longer than trees grown from grafts.
Can I grow any apple variety from seed?
Yes, but the resulting tree may not produce apples identical to the parent tree. The fruit’s characteristics can vary significantly.
What should I do if my apple seedlings are leggy?
Leggy seedlings indicate insufficient light. Increase light exposure or use grow lights to promote sturdier growth.





















