How Deep to Plant Seeds A Gardeners Guide
Factors Affecting Seed Planting Depth
How deep to plant seeds – Successful seed germination hinges significantly on planting depth. Several factors influence the optimal depth for different seeds and situations. Understanding these factors ensures higher germination rates and healthier seedlings.
Seed Size and Planting Depth
Seed size is a primary determinant of planting depth. Larger seeds, like beans or corn, generally require deeper planting to provide sufficient space for root development and access to soil moisture. Smaller seeds, such as lettuce or petunia, need to be planted more shallowly to facilitate emergence; burying them too deeply can prevent them from reaching the surface.
Soil Type and Planting Depth
Soil type significantly impacts planting depth. Loose, well-draining soils allow for slightly deeper planting as they don’t retain excess water, reducing the risk of seed rot. Conversely, heavy clay soils require shallower planting because they tend to retain moisture, increasing the risk of fungal diseases at greater depths. Sandy soils, on the other hand, might need slightly deeper planting to ensure sufficient moisture retention.
Planting Depths for Different Seed Types
A comparison of planting depths reveals the variability across seed types. Large seeds like beans (1-2 inches) require a deeper planting than small seeds like lettuce (1/4-1/2 inch). Legumes generally need slightly deeper planting than grains to accommodate their larger seed size and root systems. Consider the specific requirements of each seed type for optimal results.
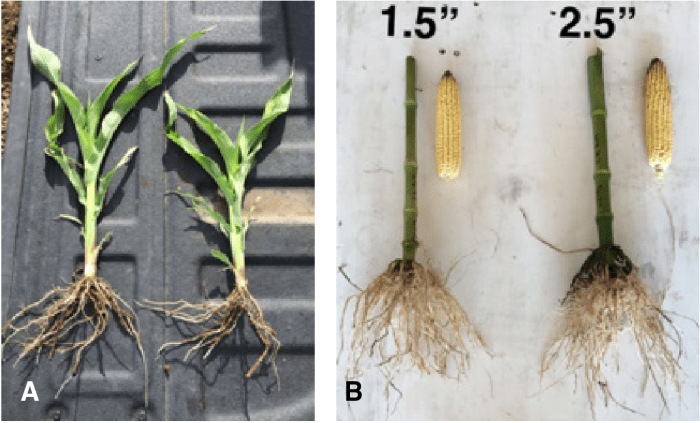
Moisture Levels and Seed Germination, How deep to plant seeds

Source: okstate.edu
Moisture plays a crucial role in seed germination. At optimal depths, seeds have access to sufficient moisture for germination, while excessive moisture at deeper levels can lead to rotting. Conversely, insufficient moisture at shallower levels can hinder germination. Finding the right balance is key.
Recommended Planting Depths for Common Vegetables
| Vegetable | Seed Size (approx.) | Recommended Planting Depth (inches) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | Small | 1/4 – 1/2 | Requires light soil and consistent moisture |
| Tomatoes | Medium | 1/2 – 1 | Can be started indoors for earlier planting |
| Beans | Large | 1 – 2 | Plant after last frost |
| Carrots | Small | 1/2 – 1 | Requires loose, well-drained soil |
Methods for Determining Planting Depth
Accurately determining planting depth is crucial for successful germination. Several techniques can be employed to ensure seeds are planted at the ideal depth for their specific needs.
Using Seed Packaging Information
Seed packets often provide recommended planting depths. Always check the packet for specific instructions as these are tailored to the particular seed variety. This is the most reliable method for determining appropriate planting depth.
Using Measuring Tools
A ruler or measuring stick offers a precise method for planting seeds at the correct depth. This is especially useful for small seeds or when planting in rows.
Using Specialized Equipment
Seed drills and other specialized planting equipment ensure uniform and precise seed placement at the desired depth. These tools are particularly beneficial for large-scale planting.
Planting Seeds by Hand
When planting by hand, create a furrow of the appropriate depth and place seeds evenly within it. Cover the seeds gently with soil and firm the soil lightly to ensure good seed-to-soil contact.
- Dig a furrow to the recommended depth.
- Space seeds evenly along the furrow.
- Gently cover seeds with soil.
- Lightly firm the soil around the seeds.
Common Mistakes in Planting Depth
- Planting too shallow: Seeds may dry out, resulting in poor germination.
- Planting too deep: Seeds may not have enough energy to reach the surface, leading to failure to germinate or weak seedlings.
- Inconsistent planting depth: Uneven planting depth results in uneven germination and growth.
Seed Germination and Planting Depth
The relationship between planting depth and seed germination is directly proportional up to a certain point. Planting at the ideal depth maximizes germination success, while deviations from this ideal negatively impact germination rates and seedling vigor.
Optimal Depth Range for Germination
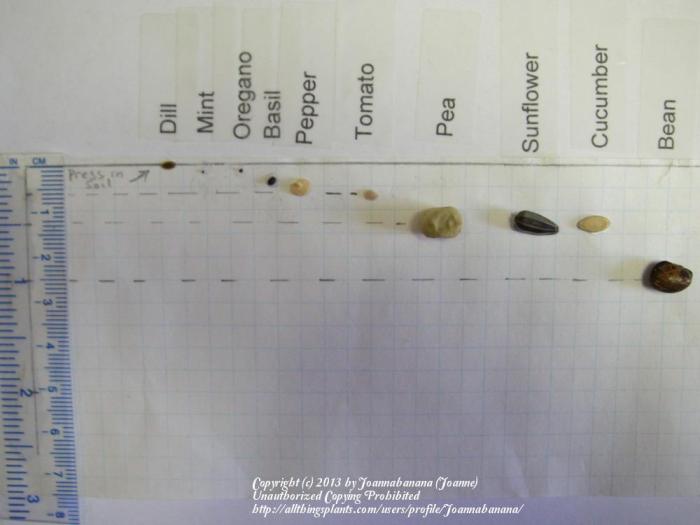
Source: garden.org
The optimal depth range varies significantly depending on seed size and type. Smaller seeds require shallower planting, while larger seeds require deeper planting to ensure sufficient resources for germination and initial growth.
Planting Depth’s Impact on Seedling Emergence
Proper planting depth ensures timely and uniform seedling emergence. Planting too shallow can result in seeds drying out before germination, while planting too deep can prevent seedlings from reaching the surface.
Effects of Incorrect Planting Depth
Planting too shallow exposes seeds to desiccation, resulting in poor germination or weak seedlings. Planting too deep deprives seeds of oxygen and light, leading to rot and failure to germinate.
Ideal vs. Too Deep Planting
Imagine a seed at the ideal depth, receiving adequate moisture and oxygen, its root pushing down and shoot emerging upward. Now, picture a seed planted too deep; it’s struggling, surrounded by dark, damp soil, unable to access sufficient oxygen and light, its energy depleted before it can even begin to germinate. The latter seed is likely to rot before it can sprout.
Specific Plant Types and Planting Depths
Recommended planting depths vary significantly across different plant types, influenced by factors like seed size, root system development, and environmental conditions. Understanding these specific requirements is essential for successful gardening.
Herbs vs. Flowers
Herbs generally require shallower planting than many flowers. Many herbs have smaller seeds that require less depth to germinate successfully, while many flowers have larger seeds that require deeper planting to access moisture and nutrients.
Specific Vegetable Planting Depths
Tomatoes are usually planted about 1 inch deep, while carrots require a depth of about 1/2 inch. Lettuce seeds are best planted about 1/4 inch deep. These depths are influenced by factors such as soil type and climate.
Planting Depth and Environmental Conditions

Source: netherlandbulb.com
Climate and environmental conditions can influence the optimal planting depth. In arid climates, deeper planting may be necessary to retain moisture, whereas in cooler climates, shallower planting might be preferable to promote faster germination.
Implications of Incorrect Planting Depth
Incorrect planting depth can lead to reduced germination rates, poor seedling vigor, stunted growth, and ultimately, reduced yields. In severe cases, it can result in complete crop failure.
Plant Types, Optimal Depth, and Consequences of Improper Depth
| Plant Type | Optimal Planting Depth (inches) | Consequences of Improper Depth |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 1/2 – 1 | Shallow: drying out; Deep: rot |
| Carrots | 1/2 | Shallow: drying out; Deep: stunted growth |
| Lettuce | 1/4 – 1/2 | Shallow: drying out; Deep: poor germination |
| Basil | 1/4 | Shallow: drying out; Deep: rot |
FAQ Summary: How Deep To Plant Seeds
What if I plant a seed too shallow?
Shallow planting can lead to seeds drying out before germination or being easily dislodged by wind or rain. Seedlings may also be more susceptible to damage from extreme temperatures or pests.
What if I plant a seed too deep?
Planting too deep can prevent the seedling from reaching the surface, leading to stunted growth or death. The seed may lack the energy to push through the soil, or it may rot due to insufficient oxygen.
How can I tell if my soil is too compact for planting?
Compact soil hinders root growth and water penetration. Try digging a small hole; if the soil resists easy penetration or the hole quickly collapses, it’s too compact. Amending with compost or other organic matter can improve soil structure.
Can I use the same planting depth for all seeds?
The ideal depth for planting seeds varies depending on the seed size; generally, plant seeds at a depth about two to three times their diameter. Knowing this depth is crucial, but equally important is understanding the optimal time to sow, especially for larger projects like lawns. To find out when the conditions are right, you might want to check this helpful resource on when can u plant grass seed before you begin.
Correct timing, coupled with proper planting depth, ensures successful germination and healthy growth.
No, planting depth varies greatly depending on seed size, type, and soil conditions. Always refer to seed packets or reliable gardening resources for specific recommendations.





















