How to Plant Maple Tree Seeds
Maple Seed Collection and Preparation
How to plant maple tree seeds – Successfully growing maple trees from seed requires careful attention to seed collection, preparation, and storage. The timing and methods employed significantly impact germination rates and overall seedling health.
Optimal Seed Collection Timing
The best time to collect maple seeds is in the late summer or early autumn, after the seeds have fully matured but before they have been dispersed by the wind or animals. This typically occurs when the seeds turn brown and the wings (samaras) are fully developed. Specific timing varies slightly depending on the maple species and local climate conditions.
For example, sugar maples typically mature in late September or early October, while red maples may mature slightly earlier.
Cleaning and Preparing Maple Seeds
Once collected, the seeds need cleaning and preparation to enhance germination. This involves removing any debris, such as leaves or twigs. Carefully separate the seeds from their wings, as the wings can hinder germination. It’s also crucial to inspect seeds for any signs of damage or disease, discarding any that appear unhealthy.
Maple Seed Stratification Methods
Stratification mimics the natural cold period seeds experience before germination. This process breaks down the seed coat’s dormancy. There are several methods:
- Cold-moist stratification: This involves mixing seeds with moist peat moss or vermiculite and storing them in a sealed container in a refrigerator at approximately 35-40°F (2-4°C) for several months.
- Outdoor stratification: Seeds can be sown directly outdoors in autumn and left to undergo natural stratification through the winter. This method requires a well-drained location to prevent rotting.
- Warm stratification (for some species): Certain maple species may benefit from a brief warm stratification period before cold stratification. This involves storing the seeds in a warm, moist environment for a short period (e.g., 2-4 weeks) before transferring them to cold stratification.
The choice of method depends on the maple species and the available resources. Always research the specific requirements for your chosen species.
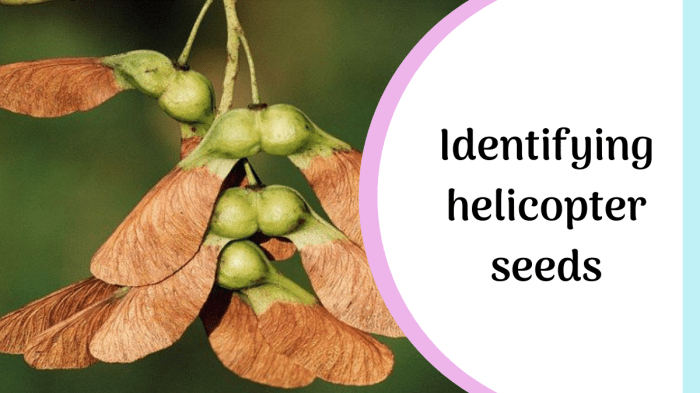
Storing Maple Seeds Before Planting
Source: mynaturenook.com
Proper storage is vital to maintain seed viability. After cleaning and preparing the seeds, store them in airtight containers in a cool, dry, and dark place. Properly stratified seeds can be stored for a short period before sowing, but it’s generally best to plant them as soon as the stratification period is complete.
Sowing Maple Seeds
Sowing maple seeds requires careful consideration of timing, soil conditions, and watering techniques to maximize germination success. The methods employed can significantly impact the success rate.
Step-by-Step Guide for Outdoor Sowing
- Prepare the soil: Loosen the soil to a depth of several inches, ensuring good drainage.
- Sow the seeds: Sow the seeds at a depth of about ¼ to ½ inch, spacing them appropriately based on the species.
- Cover the seeds: Gently cover the seeds with soil and lightly press down.
- Water gently: Water the area thoroughly but gently to avoid dislodging the seeds.
- Mulch (optional): A light layer of mulch can help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
Ideal Soil Conditions for Maple Seed Germination
Maple seeds require well-drained, slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-7.0) that is rich in organic matter. Heavy clay soils should be amended with compost or other organic materials to improve drainage and aeration. The soil should be moist but not waterlogged.
Planting maple tree seeds requires a period of cold stratification to mimic winter conditions. This process prepares the seeds for germination. For a different approach to seed starting, you might find the detailed guide on how to plant celery seeds helpful, as it covers similar principles of soil preparation and moisture control. Returning to maples, remember consistent moisture is key after planting for successful seedling development.
Comparing Sowing Methods
Direct sowing and starting indoors offer different advantages and disadvantages.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sowing | Simpler, less labor-intensive; avoids transplant shock | Lower germination rate; susceptible to environmental factors | Suitable for larger areas, established gardens |
| Starting Indoors | Higher germination rate; greater control over environment | More labor-intensive; requires careful transplanting | Suitable for smaller areas, limited space, delicate species |
Watering Newly Sown Maple Seeds
Newly sown maple seeds require consistent moisture. Water regularly, ensuring the soil remains moist but not soggy. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to seed rot. Use a gentle watering technique to avoid dislodging the seeds.
Seedling Care and Germination
Once sown, maple seedlings require careful attention to ensure healthy growth and development. Understanding common challenges and implementing appropriate care strategies are vital for successful cultivation.
Challenges During Maple Seed Germination
Common challenges include slow germination, damping-off (a fungal disease affecting seedlings), and competition from weeds. Poor soil drainage, insufficient moisture, and extreme temperatures can also hinder germination.
Protecting Seedlings from Pests and Diseases, How to plant maple tree seeds
Seedlings can be susceptible to various pests and diseases. Regularly inspect seedlings for signs of infestation or disease. Use appropriate pest control methods (e.g., insecticidal soap) and disease management techniques (e.g., fungicides) as needed, following label instructions carefully.
Transplanting Seedlings into Individual Pots

Source: gardeningknowhow.com
Once seedlings develop a few true leaves, they can be carefully transplanted into individual pots. Gently remove the seedlings from the soil, ensuring not to damage the roots. Plant them in a suitable potting mix, ensuring adequate spacing. Water gently after transplanting.
Ideal Light and Temperature Conditions for Seedling Growth
Maple seedlings require adequate sunlight, typically 6-8 hours per day. They thrive in temperatures ranging from 65-75°F (18-24°C). Protect seedlings from extreme temperatures, frost, and intense sunlight, particularly during the early stages of growth.
Transplanting Seedlings Outdoors
Successfully transplanting maple seedlings requires careful timing, site preparation, and post-transplant care. The proper technique ensures the seedlings establish well and thrive in their new location.
Optimal Transplanting Time
The best time to transplant maple seedlings outdoors is typically in spring or early autumn, after the last frost but before the ground freezes. This allows the seedlings sufficient time to establish roots before experiencing harsh weather conditions. The specific timing depends on the species and the local climate.
Preparing the Planting Site
Prepare the planting site by loosening the soil to a depth of at least 12 inches. Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve drainage and fertility. Remove any weeds or other competing vegetation.
Transplanting Process
Dig holes slightly larger than the root balls of the seedlings. Carefully remove the seedlings from their pots, ensuring not to damage the roots. Plant the seedlings at the same depth they were growing in their pots. Fill the holes with soil, gently firming the soil around the roots. Water thoroughly after transplanting.
Post-Transplant Care
- Water regularly, especially during dry periods.
- Mulch around the base of the seedlings to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Fertilize sparingly, using a balanced fertilizer appropriate for trees.
- Protect seedlings from pests and diseases.
- Monitor growth and address any issues promptly.
Maple Tree Species and Their Needs
Different maple species have varying planting requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for successful cultivation and ensures the chosen species thrives in the specific environment.
Comparing Maple Tree Species

Source: staticflickr.com
Sugar maples, red maples, and Japanese maples represent a range of growth habits and environmental preferences. Sugar maples are known for their slow growth and preference for cooler climates and well-drained soils. Red maples are more adaptable, tolerating a wider range of soil conditions and climates. Japanese maples are prized for their ornamental value but require more specific conditions, such as well-drained soil and partial shade.
Maple Species Requirements
| Species | Soil | Sun | Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar Maple | Well-drained, slightly acidic | Full sun to partial shade | Moderate |
| Red Maple | Well-drained, adaptable to various soil types | Full sun to partial shade | Moderate to high |
| Japanese Maple | Well-drained, acidic to neutral | Partial shade to full shade | Moderate |
Unique Challenges per Species
Sugar maples can be challenging to grow from seed due to their slow germination and specific soil requirements. Red maples are relatively easy to grow but can be susceptible to certain diseases. Japanese maples are more sensitive to environmental stresses, such as drought and extreme temperatures.
Selecting the Right Maple Tree Species
Consider the climate, soil conditions, and available sunlight when selecting a maple species. Research the specific requirements of each species to ensure it will thrive in the chosen location. Local nurseries can provide valuable guidance on suitable species for your area.
Troubleshooting and Problem Solving
Despite careful planning, challenges can arise during maple seed planting. Recognizing these issues and implementing appropriate solutions is crucial for success.
Common Problems and Solutions
Poor germination can result from improper stratification, poor soil drainage, or insufficient moisture. Seedling blight, a fungal disease, can be addressed through the use of fungicides and improved soil drainage. Pest infestations can be managed through the use of appropriate insecticides or other pest control methods. Environmental challenges, such as drought or frost, can be mitigated through proper watering practices, mulching, and site selection.
Troubleshooting Guide
Poor germination: Check for proper stratification, soil drainage, and moisture levels. Resow seeds if necessary.
Seedling blight: Use fungicides as directed and improve soil drainage.
Pest infestations: Identify the pest and use appropriate control measures.
Drought stress: Water regularly, especially during dry periods. Use mulch to retain moisture.
Frost damage: Protect seedlings from frost with appropriate coverings.
Visual Guide to Maple Seed Planting
Understanding the visual characteristics of healthy maple seeds and seedlings at various stages is essential for successful cultivation. Paying attention to details like color, texture, and shape can help in identifying potential problems and ensuring healthy growth.
Appearance of Healthy Maple Seeds and Seedlings
Healthy maple seeds are typically brown and have fully developed wings. Healthy seedlings initially display a pair of cotyledons (seed leaves) followed by the development of true leaves. The cotyledons are typically oval and fleshy, while the true leaves are more characteristic of the species, showing the serrated edges and specific leaf shapes of different maple species. The color of healthy leaves varies by species but should be a vibrant green, free from spots or discoloration.
The stems should be firm and green.
Parts of a Maple Seed and Seedling
A maple seed consists of a seed body containing the embryo and a wing that aids in dispersal. A seedling consists of the roots, stem, and leaves. The roots anchor the seedling and absorb water and nutrients. The stem supports the leaves and transports water and nutrients. The leaves are the primary sites of photosynthesis.
Planting a Maple Seed: A Sensory Description
The process begins with the smooth, papery texture of the samara wing as you gently separate it from the seed. The seed itself feels firm and slightly rounded. As you plant it, you feel the cool, damp soil between your fingers, and the subtle scent of earth and decaying leaves fills the air. You carefully cover the seed with soil, feeling the slight resistance as you press down gently.
Ideal Environment for a Maple Seedling
The ideal environment for a maple seedling is one where the soil is rich, dark, and moist, with a soft, spongy texture. The leaves of a healthy seedling are a bright, vibrant green, smooth to the touch, and unblemished. The air is fresh and slightly humid, and the gentle warmth of the sun encourages steady growth.
FAQ: How To Plant Maple Tree Seeds
Can I use maple seeds from store-bought maple syrup?
No, seeds from commercially processed maple syrup are not viable for planting.
How long does it take for maple seeds to germinate?
Germination time varies depending on the species and stratification method, but it can take several weeks to several months.
What should I do if my maple seedlings are leggy?
Leggy seedlings indicate insufficient light. Increase light exposure or move them closer to a light source.
My maple seedlings have yellowing leaves. What’s wrong?
Yellowing leaves can be caused by overwatering, underwatering, nutrient deficiencies, or disease. Check soil moisture, adjust watering, and consider a balanced fertilizer.





















