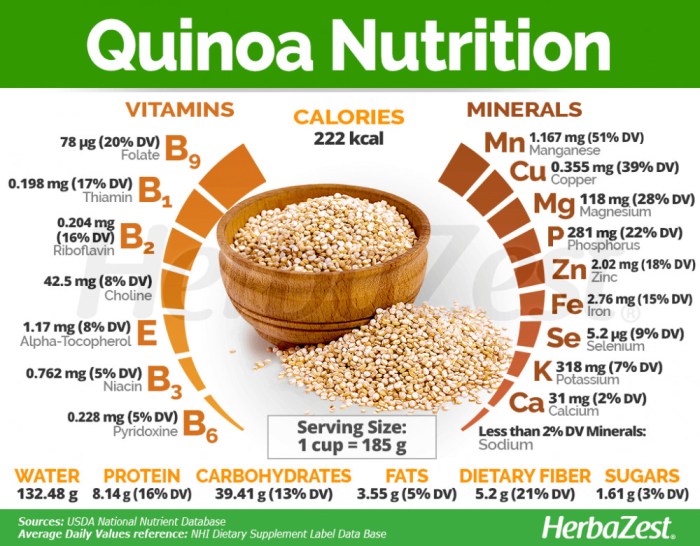
Nutritional Profile of Uncooked Quinoa
Uncooked quinoa nutrition facts – So, you’ve got a bag of quinoa staring back at you, and you’re wondering, “Is this little grain actually as super as everyone says?” Well, buckle up, buttercup, because we’re about to dive headfirst into the nutritional wonderland that is uncooked quinoa. Prepare for a data-driven adventure!
Macronutrient and Micronutrient Composition of Uncooked Quinoa
Let’s get down to the nitty-gritty. This table breaks down the nutritional power packed into 100 grams of uncooked quinoa. Remember, these are approximate values and can vary slightly depending on the source and growing conditions. Think of it as a nutritional ballpark figure – it’s close enough to give you a good idea.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value (approx.) | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 64g | 21% | Provides sustained energy, fiber for gut health. |
| Protein | 14g | 28% | Essential for building and repairing tissues, supports muscle growth. |
| Fat | 2g | 3% | Healthy fats contribute to cell function and hormone production. |
| Fiber | 7g | 28% | Promotes digestive regularity and helps you feel full. |
| Iron | 2.8mg | 16% | Essential for oxygen transport in the blood, prevents anemia. |
| Magnesium | 118mg | 28% | Supports bone health, muscle function, and blood sugar control. |
| Manganese | 1.97mg | 98% | Acts as an antioxidant, supports bone health and metabolism. Whoa, that’s a lot! |
| Phosphorus | 310mg | 31% | Crucial for bone health, energy production, and cell signaling. |
| Zinc | 2.0mg | 18% | Supports immune function, wound healing, and cell growth. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.3mg | 15% | Important for brain development and function, red blood cell formation. |
Amino Acid Profile of Uncooked Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids our bodies can’t produce on their own. This is a big deal, because many plant-based proteins are lacking in one or more of these crucial building blocks. Quinoa’s amino acid profile is pretty darn impressive, making it a fantastic protein source for vegetarians and vegans alike.
It’s like nature’s perfectly balanced protein smoothie, only without the weird green color.
Nutritional Comparison of Uncooked Quinoa to Other Grains
Let’s pit our quinoa champion against some other grain giants: rice and wheat. While all three offer carbohydrates and some nutrients, quinoa shines with its higher protein content and more complete amino acid profile. Rice is generally lower in protein and lacks some essential amino acids. Wheat, while a good source of fiber, often contains gluten, a problem for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Quinoa, being gluten-free, is a much more inclusive choice. Think of it as the Goldilocks of grains – just right!
Quinoa’s Glycemic Index and Impact on Blood Sugar

So, you’re ready to dive into the fascinating world of quinoa’s glycemic index (GI)? Buckle up, because it’s less of a rollercoaster and more of a gentle, nutrient-packed glide down a healthy hill. Unlike some carbs that send your blood sugar soaring like a rocket, quinoa takes a more measured approach, making it a friend to your pancreas (and your waistline!).Uncooked quinoa boasts a relatively low glycemic index, typically ranging from 53 to 57.
This means it doesn’t cause a rapid spike in blood glucose levels after consumption. Think of it as the Goldilocks of carbohydrates – not too fast, not too slow, just right for a steady release of energy. This moderate GI is partly due to its fiber content, which acts like a tiny brake pedal on sugar absorption.
Uncooked quinoa is packed with protein and fiber, making it a superfood! Want to compare its nutritional profile to other healthy options? Check out the northstar cafe nutrition facts for a tasty contrast. Then, you can really appreciate how uncooked quinoa shines with its impressive nutrient density – it’s a real winner for a healthy lifestyle!
Quinoa Preparation and Glycemic Index
The way you prepare quinoa can subtly influence its GI. Cooking quinoa increases its digestibility, leading to a slightly higher GI compared to the raw version. Soaking quinoa before cooking, however, might help to slightly reduce the GI, though the effect is often minimal and the benefits might not be significant enough to justify the extra step for most people.
Think of it like this: cooking is like taking the training wheels off your sugar absorption – it’s a bit faster. Soaking is like slightly adjusting the tire pressure – a tiny tweak, but maybe not earth-shattering.
Quinoa’s Benefits for Diabetes Management
For individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, quinoa’s low-to-moderate GI is a major plus. The slower release of glucose into the bloodstream helps prevent those dramatic blood sugar fluctuations that can be challenging to manage. Combined with its impressive protein and fiber content, quinoa offers a satisfying and sustainable energy source, helping to keep hunger at bay and preventing those blood sugar crashes that leave you feeling sluggish and reaching for sugary treats.
Imagine it as a superhero cape for your blood sugar, offering consistent protection and preventing any villainous spikes. Of course, quinoa alone isn’t a magic bullet for diabetes management – it’s best incorporated into a balanced diet and lifestyle plan alongside regular exercise and medical supervision.
Potential Allergens and Considerations for Dietary Restrictions

So, you’re thinking about adding quinoa to your diet – smart move! It’s packed with nutrients and tastes pretty darn good, but before you go quinoa-crazy, let’s talk about a few things that might make you think twice (or at least check the label). We’ll cover potential allergens, how to handle gluten sensitivities, and quinoa’s compatibility with various diets.
Buckle up, it’s going to be a bumpy ride (but a delicious one!).Quinoa, despite its overall health halo, isn’t entirely allergy-free. While quinoa allergies are relatively rare compared to common allergens like peanuts or milk, they do exist. The most common culprits are proteins found within the quinoa grain itself. Reactions can range from mild (itching, hives) to severe (anaphylaxis), so if you have a history of food allergies, it’s always wise to introduce quinoa slowly and monitor your body’s response.
If you experience any unusual symptoms after eating quinoa, seek medical advice. It’s better to be safe than sorry, especially when dealing with something that could potentially send you to the ER faster than a speeding bullet.
Quinoa and Gluten Sensitivity/Celiac Disease
Quinoa is naturally gluten-free, making it a fantastic alternative for people with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. However, cross-contamination during processing can occur. To ensure you’re getting a truly gluten-free quinoa, look for certified gluten-free products. These products undergo rigorous testing to guarantee they meet strict gluten standards. Don’t just rely on the label saying “gluten-free”; the certification provides an extra layer of assurance.
Think of it as quinoa’s “gluten-free superhero cape.”
Quinoa’s Suitability for Various Diets
Quinoa’s versatility shines through its adaptability to a wide range of dietary restrictions. Let’s break down its compatibility:
- Vegan: Quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. This makes it a fantastic protein source for vegans, who often need to combine different plant-based proteins to get the full spectrum of amino acids. Think of quinoa as the ultimate vegan protein power-house.
- Vegetarian: Similar to vegans, vegetarians can benefit greatly from quinoa’s complete protein profile and its fiber content. It’s a versatile addition to any vegetarian meal plan.
- Paleo: While some debate exists within the paleo community about quinoa’s place in the diet (due to its status as a seed, not strictly a vegetable), many paleo followers happily include it. It’s high in nutrients and fits well into a balanced paleo meal plan. Just be sure to follow the specific guidelines of your chosen paleo approach.
Storage and Shelf Life of Uncooked Quinoa: Uncooked Quinoa Nutrition Facts

So, you’ve got a pantry full of quinoa – the superfood champion of the grain world (or is it a seed? Let’s not get into that botanical debate right now). But how long does this nutritional powerhouse stay fresh? Fear not, quinoa connoisseur, for we’re about to delve into the secrets of proper storage and extend the shelf life of your quinoa stash.
Think of it as a quinoa-preservation mission of epic proportions!Proper storage is key to keeping your quinoa at its peak nutritional performance and preventing it from becoming a sad, stale, and potentially moldy mess. Imagine the disappointment! We’ll explore optimal storage conditions to ensure your quinoa remains a vibrant, delicious, and healthy addition to your culinary adventures.
Optimal Storage Conditions for Uncooked Quinoa
To keep your quinoa happy and healthy, think cool, dark, and dry. Storing it in an airtight container in a cool, dark pantry is the quinoa equivalent of a five-star resort. Avoid storing it in areas with high humidity, like near the sink or in a damp basement – unless you enjoy the thrill of a potential moldy surprise.
A well-sealed container will also protect your quinoa from absorbing any unwanted odors from its neighbors in the pantry. Think of it as a tiny, grain-filled fortress against pantry invaders!
Shelf Life of Uncooked Quinoa Under Various Storage Conditions, Uncooked quinoa nutrition facts
Generally, uncooked quinoa stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark, and dry place will retain its quality for about one to two years. Think of it as a two-year culinary adventure! However, if stored improperly – say, in a humid environment or an open container – you might find its shelf life significantly reduced, leading to a less-than-desirable texture and possibly, unpleasant aromas.
Think of it as a rapid decline in the quinoa’s five-star rating.
Infographic: Optimal Quinoa Storage Practices
Imagine a simple graphic. At the top, a vibrant, healthy bowl of quinoa. Below that, a three-panel illustration.Panel 1: Shows a bag of quinoa sitting sadly in a humid environment next to a leaky pipe, with mold growing on the bag. The caption reads: “NO! Damp and exposed: Short shelf life, high mold risk!”Panel 2: Shows a bag of quinoa in a damp basement, next to a pile of old potatoes.
The caption reads: “NO! Humid and unsealed: Quinoa’s worst nightmare!”Panel 3: Shows a bag of quinoa nestled snugly in a sealed container in a cool, dark pantry. The caption reads: “YES! Cool, dark, and sealed: Maximum freshness, minimum fuss!”
Key Questions Answered
Is quinoa a complete protein?
Yeah, totally! It’s one of the few plant-based foods that’s a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids your body needs.
Does quinoa have gluten?
Nope, it’s naturally gluten-free, making it a great option for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Can I eat quinoa raw?
While technically you
-can*, it’s not recommended. Cooking quinoa makes it easier to digest and unlocks its full nutritional potential. Think of it like this: raw quinoa is like a locked vault; cooking is the key to all that goodness inside.
How long does uncooked quinoa last?
Stored properly in an airtight container in a cool, dark place, uncooked quinoa can last for about a year. Keep it away from moisture and strong smells.